Table of Contents
Understanding Salivary Glands and Their Functions
Salivary glands play a crucial role in oral health and digestion.
Humans have three major pairs of salivary glands: the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands, along with numerous smaller ones.
These glands produce saliva, which helps moisten food, initiate digestion, and protect the mouth against infections.
However, various issues can affect these glands, leading to discomfort and health problems.
Common Salivary Gland Problems
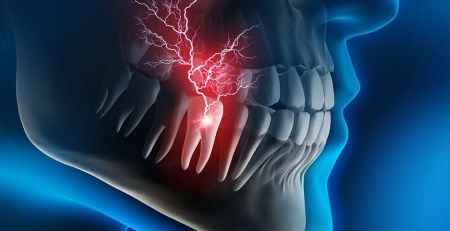
1) Salivary Gland Infections
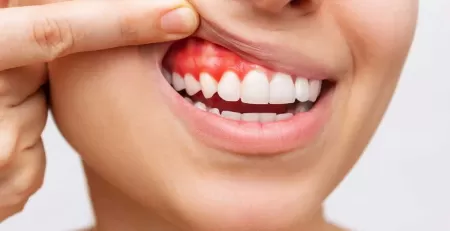
Infections, often bacterial or viral, can cause swelling and pain in the salivary glands.
Bacterial infections typically occur when the ducts that transport saliva become blocked.
One common bacterial infection is sialadenitis, which can cause painful swelling, redness, and sometimes pus.
Viral infections like mumps can also affect salivary glands, leading to significant swelling and other systemic symptoms.
2) Salivary Stones (Sialolithiasis)
Salivary stones, or sialoliths, are calcified structures that form in the salivary ducts, blocking the flow of saliva and leading to swelling and pain, especially during meals.
They can sometimes be felt as hard lumps under the skin.
Treatment often involves massaging and applying heat to the area, increasing fluid intake, or surgical removal in severe cases.
3) Sjögren’s Syndrome
Sjögren’s Syndrome is an autoimmune disorder that targets the glands that produce moisture, including salivary glands.
It results in symptoms like dry mouth and difficulty swallowing and can affect other organs.
Diagnosis is typically made via blood tests, biopsies, or imaging studies, and treatment focuses on managing symptoms.
4) Salivary Gland Tumors
Though most salivary gland tumours are benign, some can be malignant.
Symptoms might include a painless lump in the area of the ear, cheek, jaw, lip, or inside the mouth.
Treatment depends on the type of tumour and may include surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
Diagnosis of Salivary Gland Disorders
Clinical Examination and History
Diagnosing salivary gland problems involves a thorough clinical examination and reviewing the patient’s medical history.
Symptoms like pain, swelling, dry mouth, and difficulty swallowing provide crucial clues.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies such as X-rays, ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans can help identify the salivary glands’ stones, tumours, or other structural anomalies.
Biopsy
In cases where a tumour is suspected, a biopsy may be necessary to determine if the growth is benign or malignant.
Treatment and Management
Medication
For infections, antibiotics or antivirals are commonly prescribed. In cases of autoimmune disorders, medications that stimulate saliva production or manage the immune response may be used.
Surgery
Surgical interventions might be necessary for removing stones, tumours, or other treatments that have failed.
Lifestyle Modifications
Staying hydrated, practising good oral hygiene, and regular dental check-ups can help prevent some salivary gland problems.
For those with dry mouth, avoiding medications that reduce saliva production, using saliva substitutes, and chewing sugar-free gum can be beneficial.
Do Dentists See Patients For Salivary Gland Issues?
Dentists can initially evaluate patients with salivary gland problems, as they are well-versed in oral health issues.
A dentist can identify signs and symptoms of salivary gland disorders, such as swelling, pain, dry mouth, or salivary stones, during a dental examination.
Dentists are skilled in diagnosing various conditions related to the mouth and associated structures, and salivary gland issues often fall within this scope.
However, depending on the complexity and severity of the condition, dentists may refer patients to a specialist.
Oral and maxillofacial surgeons typically handle more complicated cases of salivary gland problems, especially those requiring surgical intervention.
For issues related to systemic diseases like Sjögren’s Syndrome, patients might be referred to a rheumatologist or other appropriate specialists.
An otolaryngologist (ENT specialist) might also be consulted for certain salivary gland conditions.
In summary, while dentists can serve as the first point of contact for salivary gland issues, they often collaborate with or refer patients to specialists for advanced diagnosis and treatment.

The Importance of Salivary Gland Health
Salivary gland problems, though often treatable, can significantly impact quality of life and overall health.
Understanding these issues, their symptoms, and treatment options is crucial.
Anyone experiencing persistent problems with their salivary glands should consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Maintaining the health of your salivary glands is an essential aspect of oral health and general well-being.
Article Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Always consult a healthcare professional for any medical concerns. The information is provided without any representations, warranties, or guarantees of accuracy or completeness.
Reliance on any information in this article is solely at your own risk. We are not liable for any loss or damage arising from its use.