Table of Contents
Stress is a common part of life that can profoundly impact our well-being. It’s no surprise that stress can also affect our oral health.
The connection between stress and oral health is well-established, and understanding this relationship can help us take proactive steps to maintain a healthy mouth.
The Connection of Stress and Bruxism (Teeth Grinding)
One of the primary ways anxiety affects oral health is through bruxism, commonly known as teeth grinding. This habitual act, often exacerbated by increased anxiety levels, can result in physical damage to the teeth, including wear, fractures, and loosening.
The constant pressure and grinding can wear down tooth enamel, leading to tooth sensitivity, cracks, and even fractures. Additionally, bruxism can cause jaw pain, headaches, and temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders.
Dry Mouth
Anxiety often leads to a dry mouth, characterised by reduced saliva production. Saliva plays a critical role in neutralising acids and cleansing the mouth.
When production decreases, individuals become more susceptible to cavities and tooth decay because food particles and bacteria are not adequately washed away.
Dry mouth also paves the way for a higher risk of infections due to a weakened immune response.
Gum Disease Caused by Weakened Immune Response
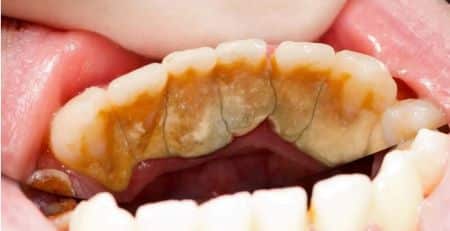
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is a significant oral health issue that stress can influence. Stress affects the body in numerous ways, one of which is weakening the immune system.
A robust immune system is crucial for fighting off various infections, including those that affect the gums. When the immune system is compromised due to stress, the body’s ability to combat gum infections diminishes, making the gums more susceptible to disease.
The initial stage of gum disease is gingivitis, characterised by swollen, red, and bleeding gums. These symptoms occur because the body attempts to fight off the bacteria in plaque, a sticky film that continuously forms on the teeth.
If plaque is not adequately removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar, further irritating the gum line.
As stress impairs the immune response, the body becomes less effective at managing the bacteria and inflammation in the gums. This can lead to the progression of gingivitis to more advanced stages of gum disease, known as periodontitis.
In periodontitis, the gums begin to pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected. The immune system fights the bacteria as the plaque spreads below the gum line. However, this response is weakened under stress, and the body’s natural defences can become overwhelmed.
In the advanced stages of periodontitis, the bones, gums, and tissues that support the teeth are destroyed. This destruction can lead to teeth becoming loose and may eventually result in tooth loss.
The chronic inflammation associated with gum disease can also have systemic effects, potentially impacting overall health.
To mitigate the impact of stress on gum health, it is essential to maintain good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing and flossing, and to seek regular dental care for professional cleanings and check-ups.
Additionally, finding effective ways to manage stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and possibly counselling can help maintain oral health and overall well-being.
Plaque
As anxiety escalates, individuals might neglect their daily oral hygiene routines, which fosters plaque buildup, increased risk of gum disease, and tooth decay.
This can result in an accumulation of plaque and tartar, leading to tooth decay and gum problems.
Canker Sores
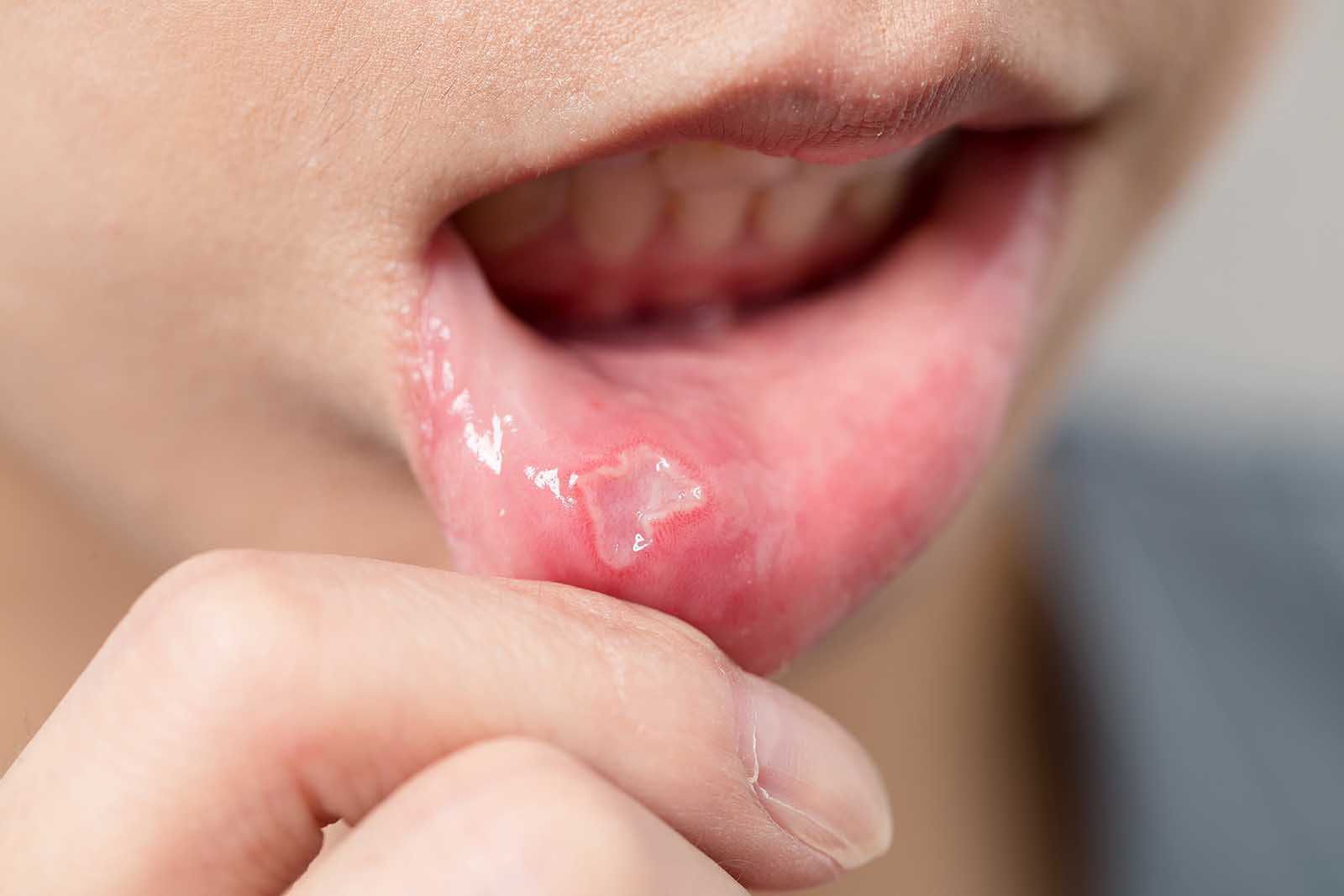
Canker sores, or aphthous ulcers, are small, shallow lesions in the mouth, typically on the inside of the lips, cheeks, the base of the gums, or under the tongue.
These sores are oval or round with a white or yellow centre and a red border. They differ from cold sores caused by the herpes virus and typically appear on the lips; canker sores are not contagious.
Stress is a significant trigger for the development of canker sores. When an individual is under stress, the body’s immune system can be compromised, which may reduce its ability to prevent these ulcers from forming.
Stress can also lead to hormonal fluctuations and changes in eating habits, such as increased consumption of acidic or spicy foods, which can irritate the mouth and potentially develop canker sores.
Additionally, stress often leads to a decrease in saliva production. Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health, as it helps to neutralise acids, wash away food particles, and keep the mouth moist, preventing irritation.
A reduction in saliva can make the oral environment more susceptible to the development of canker sores.
While canker sores are not dangerous, they can be uncomfortable and interfere with eating, speaking, and brushing teeth. They usually heal on their own within one to two weeks.
However, their presence can indicate elevated stress levels, which might impact oral health and well-being.
Addressing stress is vital to managing canker sores and preventing their occurrence. Techniques like meditation, regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and proper nutrition can help manage stress levels.
The Connection Between Anxiety and Stress with Alcohol and Tobacco
Individuals grappling with anxiety might increase their consumption of substances such as tobacco and alcohol, known adversaries of oral health. This escalation fosters a conducive environment for oral health issues and heightens the risk of developing oral cancers.
These behaviours harm oral health, including an increased risk of tooth decay, gum disease, and oral cancer.

If you or someone you know is experiencing anxiety and is concerned about its potential effects on oral health, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider and a dental professional for personalised advice and treatment.
Adopting stress management techniques and prioritising self-care are vital to mitigating the impact of stress on oral health.
Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help alleviate stress and its effects on oral health.
Maintaining a regular oral hygiene routine is crucial. This includes brushing twice daily, flossing daily, and visiting the dentist for routine check-ups and cleans.
If you are experiencing stress-related oral health issues, it is essential to seek professional dental care.
A dentist can assess your oral health and provide appropriate treatments.
In conclusion, stress can significantly impact oral health, leading to issues such as teeth grinding, gum disease, and poor oral hygiene habits.
Recognising the connection between stress and oral health and taking proactive measures to manage stress and maintain good oral hygiene can help preserve a healthy smile.
Remember to prioritise self-care and seek professional dental care to address any stress-related oral health concerns.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and does not substitute for professional medical or dental advice, diagnosis, or treatment. It is always recommended to consult a qualified healthcare provider with any questions or concerns about your health and well-being, including oral health. The information contained in this article is based on current general knowledge and does not encompass specific medical conditions or treatments. Always seek the guidance of your doctor or other qualified health professional with any questions regarding your health or medical condition.