Table of Contents
What is Dental Hypoplasia?
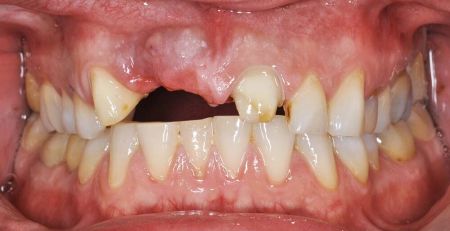
Dental Hypoplasia, also known as Enamel Hypoplasia, is the underdevelopment or incomplete development of the tooth’s enamel. This developmental disorder can occur in both primary and permanent teeth and is often recognized by pits or grooves in the teeth or even a generalized reduction in the enamel’s thickness.
Understanding Dental Hypoplasia is essential as it can lead to aesthetic concerns and functional issues like increased susceptibility to decay.
4 Symptoms of Enamel Hypoplasia

Dental Hypoplasia is a condition affecting the development of tooth enamel, leading to various dental issues.
Recognizing the symptoms is key to early diagnosis and treatment. Here’s a detailed look at the common signs of this condition.
1) Thinner and Translucent Enamel
One of the most noticeable symptoms of Dental Hypoplasia is the abnormal thinness of the tooth enamel.
In some cases, the enamel may be so thin that it appears translucent. This not only affects the aesthetic appearance of the teeth but also compromises their structural integrity.
2) Presence of Pits and Grooves
Another characteristic symptom is the development of pits or grooves on the tooth surface. These defects occur during the tooth’s formation and can vary in depth and severity.
They are not just cosmetic issues but can also make the teeth more prone to plaque accumulation and subsequent problems.
3) Increased Sensitivity to Temperature
Individuals with Dental Hypoplasia often experience heightened sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures. This increased sensitivity is due to the thinner enamel, which allows temperature changes to affect the tooth’s nerve more readily.
Consuming hot or cold foods and beverages can thus become uncomfortable or even painful.
4) Higher Risk of Cavities and Dental Decay from Enamel Hypoplasia
Finally, one of the most significant consequences of Dental Hypoplasia is an increased susceptibility to cavities and dental decay.
The compromised enamel is less effective in protecting the teeth against bacterial attacks and acid erosion, leading to a higher likelihood of developing dental caries.
What are the Causes of Dental Hypoplasia?
Dental Hypoplasia is a condition marked by underdeveloped or incomplete formation of tooth enamel. It can lead to various dental issues, and understanding its causes is crucial for prevention and management.
Here’s a closer look at the factors contributing to this condition.
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in Dental Hypoplasia. Sometimes, the condition is inherited, which can be passed down from parents to children.
Families with a history of Dental Hypoplasia may see successive generations affected by the condition.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Adequate nutrition, particularly Vitamin D and calcium intake, is crucial for healthy tooth development.
Deficiencies in these nutrients during the crucial stages of tooth formation can lead to Dental Hypoplasia.
Vitamin D and calcium are essential for solid enamel formation, and their lack can disrupt this process.
Environmental Factors
Environmental influences, especially during pregnancy, can significantly impact dental development in the fetus.
Exposure to certain toxins or infections during this critical period can interfere with the normal formation of tooth enamel, leading to Dental Hypoplasia.
Trauma During Developmental Stages
Physical injuries to the teeth during their developmental stages can also contribute to the condition.
Trauma to the teeth or jaw during infancy or early childhood, when teeth are still forming, can disrupt the normal enamel development process.
Medical Conditions in Infancy
Certain illnesses experienced during infancy can lead to Dental Hypoplasia.
Diseases that affect the body’s ability to absorb and utilize nutrients essential for tooth development can interrupt healthy enamel formation.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves a thorough dental examination. A dentist will look for the telltale signs of thinner enamel, grooves, and pits.
X-rays and other diagnostic tools may be used to determine the extent of the condition.
Treatment Options for Enamel Hypoplasia

Dental Hypoplasia, characterized by underdeveloped tooth enamel, can lead to various dental challenges. The treatment strategy for this condition is tailored to its severity and the patient’s specific needs.
Here, we explore the various treatment approaches to manage Dental Hypoplasia effectively.
Emphasizing Preventive Care
The foundational aspect of treating Enamel Hypoplasia involves preventive care. This includes regular dental check-ups to monitor the condition of the teeth and identify potential issues early.
Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial; this involves regular brushing, flossing, and possibly fluoride treatments to strengthen the enamel.
Dietary management also plays a key role, where the intake of foods and beverages high in sugar and acids is minimized to prevent cavities.
Utilizing Dental Restorations
For teeth affected by Dental Hypoplasia, dental restorations such as fillings, crowns, or veneers may be necessary. These restorations serve to improve both the appearance and functionality of the teeth.
Fillings can address cavities that may develop due to weakened enamel, while crowns and veneers provide a protective covering, enhancing the tooth’s strength and aesthetic appearance.
Considering Orthodontic Treatment
Orthodontic treatment may be recommended in more severe cases of Dental Hypoplasia, where the bite alignment is affected.
This can involve using braces or other orthodontic devices to correct alignment issues, ensuring proper bite function and reducing the risk of further dental problems.
Specialized Treatment for Sensitivity
Heightened sensitivity to temperature is a common issue associated with Dental Hypoplasia.
Managing this sensitivity is an essential aspect of treatment. This may include using specialized toothpaste designed for sensitive teeth, fluoride treatments to strengthen the enamel, and other desensitizing agents recommended by a dentist.
8 Risks of Dental Hypoplasia to Oral Health

Dental Hypoplasia can leave teeth more vulnerable to a variety of risks and complications:
1) Increased Sensitivity
Enhanced Sensitivity due to Enamel Deficiency: Dental Hypoplasia results in underdeveloped enamel, which can cause teeth to be more sensitive to temperature fluctuations and specific foods or drinks. This condition leads to discomfort and can significantly affect daily life, emphasizing the need for careful management.
2) Higher Risk of Cavities
Vulnerability to Cavities with Underdeveloped Enamel: The protective layer of enamel is crucial for tooth health. Dental Hypoplasia compromises this protection, making teeth more susceptible to cavities and decay. This highlights the importance of proactive dental care to mitigate these risks.
3) Aesthetic Impacts
Cosmetic Concerns and Self-Image: The appearance of teeth affected by Dental Hypoplasia—characterized by discoloration, pits, or grooves—can lead to self-esteem or confidence issues. This is especially true for visible teeth, underscoring the psychological and emotional dimensions of the condition.
4) Chewing Difficulties
Eating Challenges Due to Weakened Teeth: The severity of Dental Hypoplasia can impair the teeth’s ability to handle normal biting and chewing forces, complicating eating processes. This aspect of the condition can affect nutritional intake and overall quality of life.
5) Potential for Tooth Loss in Enamel Hypoplasia
Increased Likelihood of Tooth Damage and Loss: Severe cases of Dental Hypoplasia may lead to teeth that are prone to breakage or wear, raising the risk of tooth loss. This severe outcome underscores the necessity for early and ongoing dental interventions.
6) Orthodontic Challenges
Complications with Misalignment and Malocclusion: Dental Hypoplasia can sometimes co-occur with malocclusion or misaligned teeth, presenting additional orthodontic challenges. This complexity requires specialized orthodontic approaches for effective management.
7) Financial Implications
Cost Considerations in Dental Care: Addressing the effects of Dental Hypoplasia often involves extensive dental treatments, such as fillings, crowns, or other restorative procedures. These necessary interventions can lead to significant healthcare expenses, highlighting the economic impact of the condition.
8) Psychological Effects
Social and Emotional Well-Being: The noticeable impact of Dental Hypoplasia on an individual’s teeth can contribute to social anxiety and embarrassment, affecting mental health. This underscores the broad implications of the condition beyond the physical aspects, affecting individuals’ overall well-being.
Proper diagnosis and treatment by a dental professional can mitigate these risks, and preventive measures can be essential in managing the condition.

A tailored treatment plan may include regular dental check-ups, a particular at-home oral care routine, dental restorations, or cosmetic procedures to enhance the appearance and function of the affected teeth.
If you suspect you or your child may have Dental Hypoplasia, it’s essential to seek professional dental care.
At Amazing Smiles, we provide a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan to address Dental Hypoplasia.
With our experienced team, we offer the best possible care for this condition. Book a consultation today, and take the first step toward a healthy and beautiful smile.
As preferred provider dentists, we allow patients to maximize the most out of their private health benefits.
Your dream smile is within reach with Amazing Smiles!
$145 Patient Special Offer for your first check-up and clean at any of our dental clinics.